Search
Research
Standardization of Epidemiological Surveillance of Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAcute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (APSGN) is an immune complex-induced glomerulonephritis that develops as a sequela of streptococcal infections. This article provides guidelines for the surveillance of APSGN due to group A Streptococcus (Strep A). The primary objectives of APSGN surveillance are to monitor trends in age- and sex-specific incidence, describe the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with APSGN, document accompanying risk factors, then monitor trends in frequency of complications, illness duration, hospitalization rates, and mortality.

The following maps provide a visual insight into how the number and rate of Indigenous suicides varies across different regions of Australia.
When kids are having surgery, the most common problem that can occur during anaesthesia is a respiratory adverse event.

The Perioperative Medicine team has developed a unique chewable tablet that gives the child the sensation of having a full stomach, without compromising their fasting regime.

Scientific discoveries over the past 30 years mean doctors now have a deeper understanding of what causes disease and how those diseases might progress.
The WAACHS regional profiles look at all four volumes of results across the ATSIC regions of Western Australia.

A pilot clinical study has found an immunotherapy drug can dramatically increase survival rates for babies with a rare form of leukaemia, paving the way for a major international clinical trial.
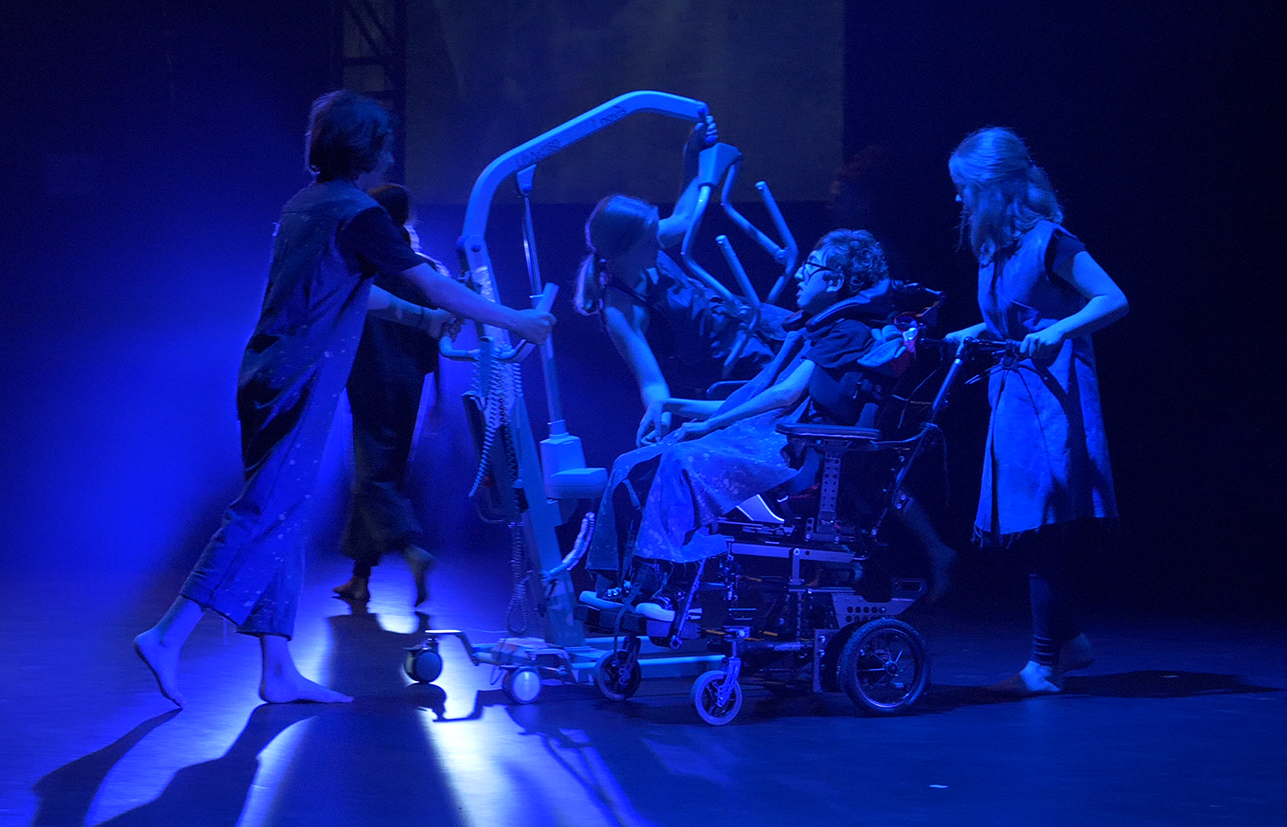

A quality of life tool developed by disability researcher Jenny Downs is helping to reveal the difference specific interventions can make to the lives of children and families living with disability.
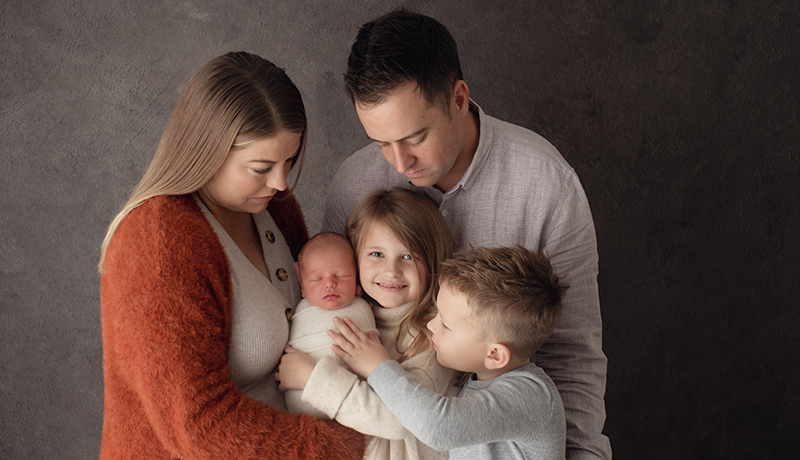

Video technology is helping researchers learn more about the earliest features of autism, and in turn is helping families gain access to better interventions.
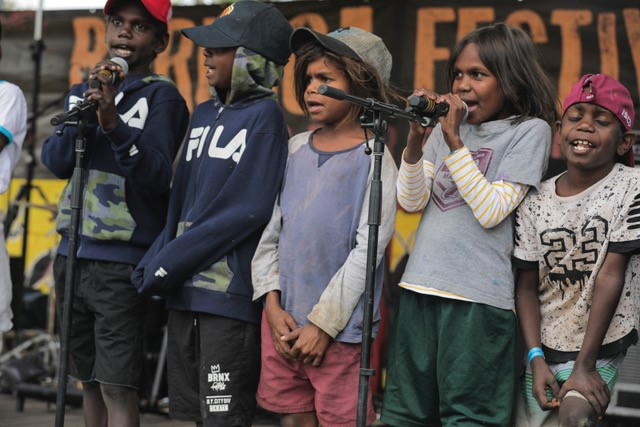

A song written by kids in Barunga as part of the END RHD Communities Project is helping prevent the spread of infections that cause rheumatic heart disease in remote Aboriginal Communities.
